Grad Student Feature: Jonathon Kotwa and Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Canids
Jonathon D. Kotwa completed his PhD in the Department of Pathobiology at the University of Guelph. His research interests include interdisciplinary perspectives for evaluating emerging zoonotic diseases, with a specific concentration on investigating the role of wild canids as sentinel species for pathogens of public health and veterinary significance.
Find out more about Kotwa’s work at EmultiOntario.com
Click here to access the OAHN infographic on E. Multilocularis in Ontario
OAHN Companion Animals Research Project 1: Investigation of the prevalence of Echinococcus multilocularis and risk of infection in wild canids in Ontario, Canada
Project lead: Andrew S. Peregrine
Collaborators: Jonathon Kotwa (OVC PhD student), Claire Jardine, David Pearl, Olaf Berke, Nicola J. Mercer, Mats Isaksson, Mikael Juremalm and Eva Osterman-Lind
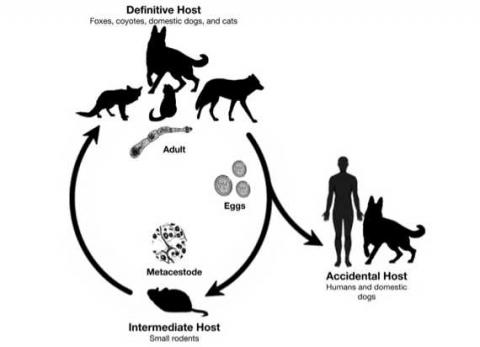
Echinococcus multilocularis is a small, zoonotic tapeworm that is typically maintained in a wildlife cycle. Ingestion of the eggs shed by definitive hosts (primarily wild canids) by humans and dogs can result in alveolar echinococcosis (AE), a disease that is potentially fatal when left untreated. Prior to 2012, Ontario was thought to be free of this parasite. Since then, cases of AE have been reported in 5 dogs, 2 lemurs, and 1 chipmunk in southern Ontario. The primary objectives of this study were to determine where in southern Ontario E. multilocularis occurs, and to elucidate risk factors associated with infection in wild canids.
From November 2015 to March 2017, rectal fecal samples collected from 460 wild canid carcasses (416 coyotes, 44 foxes) were analyzed for the presence of E. multilocularis DNA. Overall, 23% (95% confidence interval: 19-27%) of wild canids from the western, central, and eastern regions of southern Ontario tested positive. Additionally, a significant high-prevalence cluster was identified in the western-central region (Golden Horseshoe). Notably, the infection cluster coincided with areas of high human population density, suggesting that zoonotic transmission should be a public health concern. These results provide important information that can help guide public health and veterinary efforts in the development of prevention strategies, particularly in high-risk areas.